TechRisk Notes#47: The International Secure AI System Development Guide
Plus, Justin Sun's crypto firms under attack, KyberSwap’s $47M heist and OT water system hacked!
Tech Risk Reading Picks
Secure AI system development: The U.S. Department of Homeland Security's Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the UK's National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) have jointly released global guidelines for secure AI system development. These guidelines, developed in collaboration with 21 international agencies, including G7 members, aim to assist developers in making informed cybersecurity decisions throughout the AI development process. The guidelines focus on integrating "secure by design" principles, emphasizing the significance of cybersecurity in building safe, secure, and trustworthy AI systems. [more][more-2][more-guidelines-secure-AI-sysdev]
The guidance classifies these vulnerabilities within three categories: those “affecting the model’s classification or regression performance,” those “allowing users to perform unauthorized actions” and those involving users “extracting sensitive model information.”
It sets out practical steps to “design, develop, deploy and operate” AI systems while minimizing the cybersecurity risk.
Governance on AI:
According to the Stanford University’s AI index report, the number of AI incidents and controversies has risen significantly since 2012, prompting calls for regulations. Jonas Kron, chief advocacy officer at Trillium Asset Management, has been urging tech companies, including Google parent Alphabet, to provide more transparency about their AI algorithms. The concern is that AI poses governance risks, potentially reinforcing discrimination in areas like healthcare and enabling misuse of personal data. Investors in Microsoft, Apple, and Alphabet have filed resolutions for more transparency, and the AFL-CIO Equity Index Fund has asked companies, including Netflix and Walt Disney, to report on adopting guidelines to protect against AI-related harms. [more][more-AI-index-report]
Microsoft's president, Brad Smith, believes that artificial intelligence (AI) does not pose an immediate threat to humanity's existence. However, he emphasizes the need for governments and businesses to address the risks associated with AI by implementing "safety brakes”. While he doesn't foresee an existential threat in the next decade, he advocates for proactive measures to solve potential problems before they arise. [more]
OT Security - water system hacked: The Municipal Water Authority of Aliquippa in Pennsylvania experienced a cyber attack on the system which monitors and regulates water pressure for certain townships. It was quickly disabled upon detection of the intrusion. The water utility asserts that there is no known risk to the water supply or drinking water. The hack is attributed to a group called Cyber Av3ngers, linked to Iran, targeting an industrial control system (ICS) from the Israeli company Unitronics. The attackers may have taken control of a Unitronics Vision system, known for critical vulnerabilities. [more]
Web3 Cryptospace Spotlight
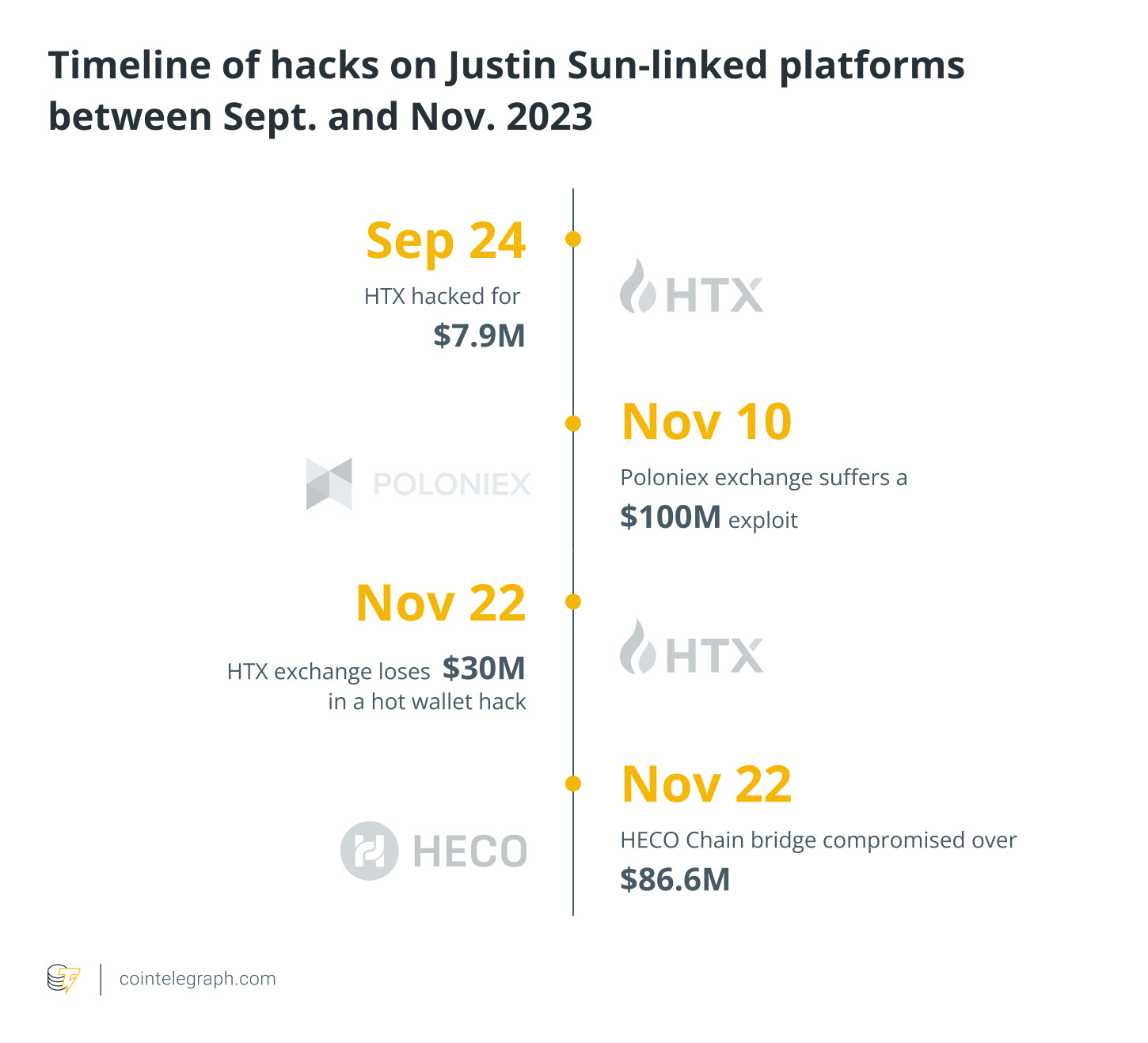
Justin Sun targeted: Tron founder Justin Sun's cryptocurrency businesses, including HTX crypto exchange and Poloniex, have been targeted by hackers in at least four attacks over the past two months. HTX was hacked twice, losing nearly $8 million in the first attack and $30 million in the second. Poloniex, owned by Sun since 2019, suffered a significant breach with attackers stealing at least $100 million in cryptocurrency. The incidents raise concerns about the security of Sun's crypto ventures [more]
KyberSwap’s heist: 23 Nov - An attacker used a sophisticated smart contract exploit, termed an "infinite money glitch", to drain $46 million from DeFi platform KyberSwap. By exploiting a bug in KyberSwap's concentrated liquidity pool feature, the attacker manipulated the system into double-counting liquidity, resulting in an unfair price for a swap. The exploit was described as a carefully engineered tactic, allowing the attacker to deceive the contract about the actual liquidity available. [more][more-2][more-3]
Security not sufficient: With almost $1 billion had already been lost to crypto hacks, exploits and scams in 2023, experts in blockchain security stressed the urgent need for prioritizing security measures in the crypto space. They recommend adopting crypto-native multifactor authentication, conducting regular security audits, and implementing comprehensive security strategies that go beyond audits. Users are encouraged to demand better security, and regulators may need to intervene if necessary. Additionally, the understanding potential security threats and employing crypto data analytics can also play a crucial role in preventing future hacks. [more]
Bitcoin’s Smart Contract: Bitcoin does support smart contracts through a scripting language called Script. While it's a misconception that Bitcoin is not Turing complete, the reason it's not commonly associated with smart contracts is due to the absence of certain opcodes. Opcodes are essential for executing functions on a blockchain, and Bitcoin's script lacks opcodes that enable reading and writing the current "state" of the blockchain. Unlike blockchains like Ethereum, where smart contracts can perform complex automated tasks, Bitcoin primarily records ownership and facilitates coin transfers with limited conditions. [more]