TechRisk #94: Vulnerable AI models
Plus, Large-scale cryptojacking attack, Laundering Lazarus' coins, $150K bug bounty prize and more!
Tech Risk Reading Picks
Over 34 security vulnerabilities in various open-source AI and machine learning models: Researchers have identified over 34 security vulnerabilities in various open-source AI and machine learning models, including ChuanhuChatGPT, Lunary, and LocalAI. These flaws could lead to remote code execution and unauthorized data access. Notably, Lunary has critical issues like Insecure Direct Object Reference (IDOR) and improper access control, both with a CVSS score of 9.1. ChuanhuChatGPT's user upload feature contains a path traversal flaw (CVE-2024-5982) with a CVSS score of 9.1, potentially allowing arbitrary code execution. Users are advised to update to the latest versions to mitigate these risks. [more][more-ProtectAI_report]
Hallucination risk in cybersecurity usage: In early 2023, Google’s AI chatbot, Bard, demonstrated a common issue with AI known as an "AI hallucination”. This happens when a large language model (LLM) provides incorrect or fabricated answers. AI hallucinations often result from training on inaccurate or biased data, which leads to flawed responses and undermines trust in AI. In cybersecurity, hallucinations can lead to missed threats or false alarms, which may either waste resources or allow real threats to go unnoticed. To mitigate these risks, organizations should train employees in prompt engineering, use clean data, and implement fact-checking. By addressing these issues, businesses can use AI effectively to enhance their cybersecurity defenses and stay ahead of cyber threats. [more]
Anatomy of an LLM RCE: There are security risks in integrating LLMs with external software components, exposing them to potential Remote Code Execution (RCE) attacks. Using an example from LoLLMs, a tool that lets LLMs perform math calculations, it demonstrates how attackers can exploit Python’s `eval()` function to bypass sandbox restrictions and execute arbitrary code. By tricking the LLM into outputting specific JSON commands, attackers can circumvent safety checks, leading to unauthorized control over the host system. The vulnerability has been patched, emphasizing the need for robust security in LLM integrations to prevent misuse. [more]
Apple’s AI bug bounty: Apple is launching its Private Cloud Compute, a private AI cloud, and offering up to $1 million to security researchers who find vulnerabilities that could compromise its security. The highest bounties are for exploits that enable remote malicious code execution. Researchers can also earn up to $250,000 for exploits that leak sensitive data or customer prompts, and up to $150,000 for accessing sensitive information from a privileged position. This extension of Apple's bug bounty program emphasizes protecting user data, extending prior efforts like their researcher-only hackable iPhone to enhance device security. [more]
Preparation for the era of quantum computing: The Pentagon's IT office is prioritizing the modernization of its cryptographic algorithms to counter vulnerabilities, especially in preparation for the era of quantum computing. Quantum computers, though a decade away, could potentially breach current encryption standards like RSA. David McKeown, Pentagon's Deputy CIO, emphasized the importance of post-quantum cryptography (PQC) for future-proofing Pentagon data and highlighted the NSA’s role in developing quantum-resistant standards. This modernization is a comprehensive effort across the Pentagon's encrypted assets to ensure they remain secure as PQC standards evolve. [more]
It was also noted that once cryptographic upgrades are underway, the next focus is on transitioning to a zero-trust cybersecurity model by 2027, a system designed to monitor user activities on the network to quickly detect and remove threats. The final priority is securing the defense industrial base, particularly through Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification (CMMC) 2.0, to protect critical infrastructure from cyber threats.
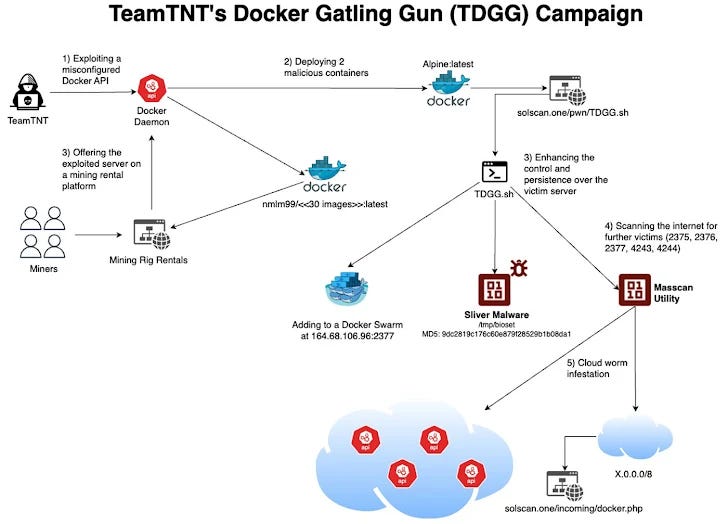
Cryptojacking group large-scale attack: TeamTNT, a notorious cryptojacking group, is prepping a large-scale campaign targeting cloud environments, specifically Docker, for cryptocurrency mining and renting out compromised servers. They exploit exposed Docker daemons to deploy malware, cryptominers, and other malicious payloads via Docker Hub, creating a Docker Swarm of infected instances. They identify exposed Docker API endpoints using tools like masscan and ZGrab, scanning over 16.7 million IP addresses. Their attack includes deploying malicious containers and scripts, such as the Docker Gatling Gun, and using the open-source Sliver C2 framework for remote control. Besides cryptomining, they rent compromised servers on Mining Rig Rentals, marking an evolution in their monetization strategy. TeamTNT also uses an anonymous DNS service, AnonDNS, for added privacy. Additionally, another attack campaign was discovered by Trend Micro, where a brute-force attempt introduced the Prometei botnet, spreading through RDP and SMB vulnerabilities for Monero mining on compromised systems. [more]
Web3 Cryptospace Spotlight
Laundering coins: Chinese OTC trader Yicong Wang allegedly laundered over $17 million for North Korea’s Lazarus Group, notorious for major crypto hacks like the $600 million Ronin bridge exploit. Active since 2022, Wang reportedly converted stolen crypto into cash through bank transfers, aiding the group in over 25 hacks. [more]
Wallet-draining scam ads: Security firm Scam Sniffer reported a deceptive misspelled Google ad promoting Sony's blockchain project, Soneium, was a phishing scheme aimed at draining crypto wallets. The ad led users to a fake site nearly identical to the official Soneium page, hiding malicious software to steal funds and bypassing Google’s security checks. This adds to a growing trend of crypto-related phishing attacks which steal $46 million in September alone. Wallet-draining schemes have caused significant financial damage in the crypto space, with hundreds of millions lost in recent years. [more]
$150K for a bug: A Web3 security researcher known as jayjonah.eth from Spearbit uncovered a critical bug in the Evmos blockchain, which could have had devastating consequences for its operations. He revealed his findings in a blog post shared on X, explaining that the vulnerability could halt the entire network. His discovery earned him a $150,000 reward from the Cosmos Network. While reviewing Cosmos documentation, jayjonah.eth identified a flaw related to "module accounts." These accounts could break the blockchain if they received funds outside predefined rules. He tested this, leading to a halt in block production and a complete stop of the Evmos chain. This bug, though seemingly simple, was a critical oversight. [more]
Interview with Cyver on WazirX hack: On the morning of July 18, WazirX crypto exchange founder Nischal Shetty received a call from Cyvers, a Web3 cybersecurity firm, alerting him to an ongoing hack. Hackers were draining $234.9 million (Rs 2000 crore) worth of crypto assets from WazirX’s multi-signature wallet, impacting 4.4 million Indian users. Despite immediate action, the funds could not be saved, and the incident’s repercussions continue as many users await access to their funds. [more]
In an interview with The Crypto Times, Cyvers VP Michael Pearl revealed that a malicious smart contract targeted WazirX’s wallet, and Cyvers’ AI-driven monitoring system detected the attack quickly. Pearl stated that such sophisticated attacks often involve well-funded groups or state-sponsored actors, not just individual hackers, possibly implicating groups like Lazarus.
Cyvers’ analysis of 61 hacking incidents in 2022-23 showed an average response time of four hours, often too slow to prevent major losses, especially as hackers strike during off-hours. Pearl expressed frustration over the lack of effective security measures and how affected companies are struggling to keep up with increasingly advanced cyber threats.