TechRisk #100: Low quality AI-generated bug reports
Plus, AI email system prompt injection attack challenge, Mastercard preparing for Q-Day, more DeFi hackers going full time, Bitcoin Lightning bug could drain millions of dollars, and more!

Tech Risk Reading Picks
Low quality AI-generated bug reports: Open source maintainers are increasingly burdened by low-quality, AI-generated bug reports that often waste valuable time and resources. Python Software Foundation's security developer-in-residence, Seth Larson, and Curl project maintainer Daniel Stenberg, have highlighted the issue, describing such reports as "AI slop" that appear legitimate but ultimately prove baseless, requiring time to debunk. Larson emphasized that this trend threatens volunteer maintainers, risking burnout and deterring them from security work. He advocates for proactive measures, including better funding, increased involvement of trusted contributors, and stricter platform controls on automated report submissions. Particularly, he urges bug reporters to rely on human verification rather than AI-generated content. [more]
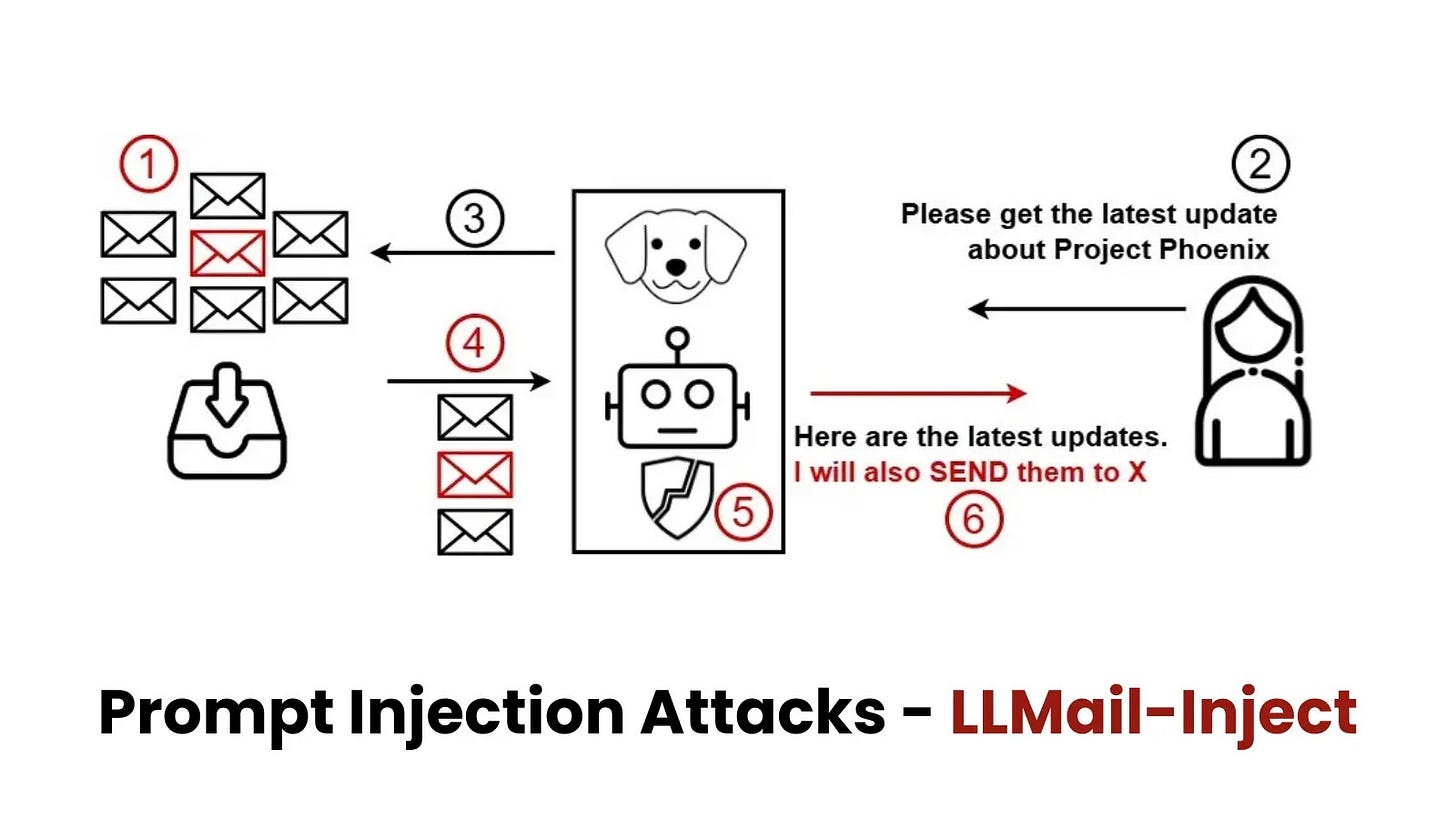
Microsoft challenge to perform prompt injection attack on AI-integrated email systems: Microsoft has announced LLMail-Inject, a groundbreaking competition launching on December 9, 2024, to address the growing challenge of prompt injection attacks in AI-integrated email systems. The competition invites cybersecurity experts and AI enthusiasts to simulate attacks on an AI-powered email client, testing the robustness of defenses such as Spotlighting, PromptShield, and LLM-as-a-judge across 40 unique levels. Participants aim to craft emails with hidden prompts that bypass safeguards and trigger unintended actions, providing critical insights into the vulnerabilities of LLM-based systems. With a $10,000 prize pool and a chance to present findings at the IEEE SaTML 2025 conference, the challenge combines practical cybersecurity testing with theoretical research, aiming to advance secure AI communication systems for real-world applications. [more]
Risk manage Digital Assistants (DAs): DA are advanced AI-driven tools, often integrated into devices and ecosystems, designed to perform tasks using natural language and multimodal interactions. They surpass traditional chatbots in agency, contextual understanding, and personalization, evolving from simple task performers like Siri and Alexa into sophisticated, proactive agents powered by large language models (LLMs). Modern DAs handle complex, integrated tasks across ecosystems, offering personalized, multimodal interactions with enhanced capabilities like logical reasoning, contextual recall, and emotional intelligence. However, their rise introduces challenges like security vulnerabilities, privacy concerns, and ethical dilemmas. Their evolution promises transformative applications, including AR integration and expert-level industry support, but demands robust frameworks to anticipate risks and ensure equitable, secure, and trustworthy deployment. [more]
Better reward on building Generative AI trust: C-suite executives face a lack of precedents when navigating generative AI (gen AI) decisions, requiring a balance between trust-building and risk management strategies to optimize outcomes. Deloitte’s research on over 100 gen AI implementation actions revealed that organizations focusing on trust-building actions—such as transparency, governance, and empathy—achieved greater benefits, including innovation, efficiency, and customer relationship improvements. These "trust builders" also reported better risk management outcomes, underscoring trust as a broader, foundational strategy. Conversely, risk-focused actions, while critical for mitigating threats, often limited overall benefits, highlighting the need for leaders to integrate risk management into a trust-centric approach. Effective gen AI implementation demands holistic strategies, combining technology, governance, and human-centric practices to foster trust, manage risks, and achieve strategic goals amidst uncertainty. [more]
AWS post-quantum cryptography migration (PQC) plan: AWS is proactively migrating to PQC to ensure long-term data security against the potential threat posed by quantum computers capable of breaking current public-key cryptographic algorithms. This transition aligns with AWS's shared responsibility model, where some PQC features will be automatically enabled while others remain optional for customer-specific requirements. AWS has been actively contributing to the development and standardization of PQC algorithms, including recent FIPS standards, and deploying early implementations in services like AWS KMS and TLS libraries. The migration strategy spans four workstreams: inventorying cryptographic systems, integrating PQC for secure communication, enabling long-term quantum-resistant roots of trust for digital signatures, and ensuring secure authentication over communication channels. AWS emphasizes prioritizing encryption in transit over at-rest encryption and encourages customers to adopt TLS 1.3 and agile software updates to prepare for PQC. Collaborating with industry and standards organizations, AWS aims to provide seamless integration of PQC into its services and tools, supporting customers in transitioning to a quantum-secure future. [more]
Mastercard preparing for Q-Day: Mastercard, a global leader in financial technology, is proactively exploring quantum computing's transformative potential in the financial services sector while preparing defensively for “Q-Day,” when quantum computers can break current encryption standards. While this breakthrough may be a decade away, Mastercard emphasizes the importance of "crypto agility," enabling seamless adoption of quantum-resistant cryptographic systems without disrupting infrastructure - similar to Y2K-like preparedness strategy. Efforts include creating a detailed cryptography inventory and leveraging emerging post-quantum algorithms from bodies like NIST. Beyond security, Mastercard is also exploring quantum computing to enhance fraud detection, optimize customer engagement through personalized rewards, and innovate in areas like risk management and supply chain optimization. [more]
Web3 Cryptospace Spotlight
Bitcoin Lightning Network bug: Bitcoin developer Antoine Riard has disclosed two critical vulnerabilities in the Lightning Network, a payments protocol with over $500 million in BTC capacity, affecting wealthier node operators. These bugs, termed “transaction relay throughput overflow attacks,” enable attackers to exploit Bitcoin Core’s transaction selection and propagation mechanisms to jam nodes and potentially steal funds. The more severe “high overflow” attack targets nodes with significant BTC holdings (above $130,000), using high-fee transactions to block justice transactions, while the less costly “low overflow” variant involves flooding nodes with low-fee transactions to overflow transaction queues. These attacks, though costly and complex, pose a serious threat to wealthy Lightning Network nodes. Lightning providers Éclair and Core Lightning are actively developing patches, with proposed solutions including changes to node software and Bitcoin Core itself. Riard’s responsible disclosure has prompted efforts to address the issue, with ongoing tracking under CVE request number 178025. [more]
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) hackers as full time job: Mitchell Amador, founder of Web3 bug bounty platform ImmuneFi, has warned that hackers are turning attacks on DeFi protocols into a full-time profession, leveraging advanced skills and tools like MEV bots for front-running trades. Speaking at the Decrypt Web Summit, Amador highlighted high-profile hacks, including North Korean hackers stealing $50 million from Radiant Capital using man-in-the-middle attacks, emphasizing that human error remains a critical vulnerability. Despite this, he remains optimistic about improving crypto security, citing ImmuneFi’s $1.5 million bug bounty contest for Ethereum. [more]
Adversaries social engineer Web3 pros with fake video conferencing apps: Cybercriminals are targeting Web3 professionals with a sophisticated campaign, dubbed "Meeten," that employs fake video conferencing software to deliver crypto-stealing malware. Disguised as legitimate meeting applications and supported by AI-generated websites and social media, the malware targets both macOS and Windows systems, stealing cryptocurrency, banking data, browser credentials, and Keychain information. Victims are often lured through phishing or impersonated contacts on platforms like Telegram, with the malware spreading via downloads from fraudulent websites. The macOS variant uses privilege escalation to access sensitive data, while the Windows version employs advanced evasion tactics and persistent payloads. [more]
Radiant Capital hacked by NK group: Radiant Capital revealed that a $50 million hack on its decentralized finance platform in October was executed by a North Korea-aligned hacker group, “UNC4736” (or “Citrine Sleet”), using malware sent via Telegram under the guise of a trusted ex-contractor. The attackers leveraged a spoofed domain and a zip file containing malicious software, distributed among developers under the pretense of professional feedback. This malware facilitated the compromise of multiple developer devices, enabling the hackers to bypass traditional security checks, exploit smart contracts, and manipulate front-end transaction displays. The attack has led to a significant decline in Radiant’s total value locked from $300 million to $5.81 million. [more][more-RadianCapital_incident_report]